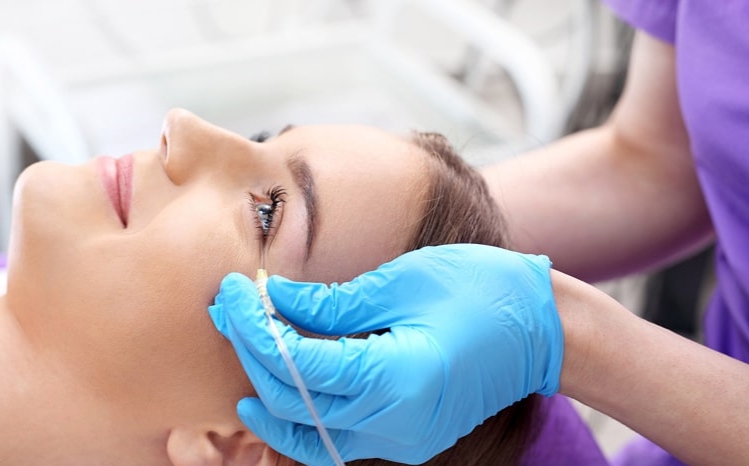
Carboxytherapy is a type of aesthetic process which is done by injecting medical gaseous carbon dioxide into the subcutaneous layer through a needle. It works by eliminating fat cells, increasing blood flow, improving skin elasticity, and significantly reduction of cellulite. There are no known and common risks associated with the carboxytherapy process. Carbon dioxide has been safely utilized for many years to facilitate endoscopic surgeries of the abdomen. Carbon dioxide is also being injected directly into the bloodstream by invasive cardiologists for certain diagnostic and therapeutic processes. There are various types of treatments depending on the severity of the problem being treated. Mostly, six to twelve treatments spaced once a week or two treatments during a week yield a perfect result. The average carboxytherapy treatment takes approximately fifteen to thirty minutes to be completed. Bruising, swelling, and redness are very common and completely normal and they will disappear in a few days following your treatment. Carboxytherapy safely can be used for treating all skin types without significant pain or downtime. It can erase years off a patient's face and is one of the most effective facial treatments for achieving a significant aesthetic improvement within 2 to 6 months the time that the effects of collagen stimulation and remodeling become evident. For new stretch marks that are not very severe, a single session of treatment can be enough. However, may need treatment once a week for 2 to 4 weeks. Older stretch marks may need 3 or 4 treatment sessions during 3 or 4 weeks. For cellulite, you should see a smoother appearance in your skin quickly. You can discuss your requirements with your skincare provider. The number of sessions and their intervals depend on your skin condition.
_Localized fat
_Cellulite
_Acne scars
_Surgical scars
_Stretch marks
_Eye wrinkles
_Rejuvenation of hands, décolletage, neck
_Psoriasis
_Nasolabial folds and peri-oral wrinkles
_Skin rejuvenation
_Skin whitening
_Raynaud’ phenomenon
_Lower limbs arterial disease and ischemia
_Erectile dysfunction with micro _vascularization disorders
_Hair loss
_Needle phobia
_Stress, with history of vagal _unconsciousness event
_Severe heart failure, congestive heart disease
_Recent heart attacks and unstable angina pectoris
_Restrictive pulmonary disease, chronic obstructive lung disease
_Sleep apnea
_Renal failure, dialysis
_Recent cerebrovascular accident
_Uncontrolled blood pressure
_Immunosuppression or deficiency
_Patients with impaired healing
_Connective tissue disorders or diseases
_Bleeding disease: Willebrand’s disorder, hemophilia
_Bacterial infection: dermatitis, cellulitis
_Foreign body in the area to be treated (jewelry or implants)
_Herpes simplex in the acute phase and other acute skin viral infections
_Skin disease with abnormally increases local circulation
_Facial rosacea
_Poikiloderma of cavit
_Pregnancy
_Lactation
_Anticoagulation, recent aspirin, or anti-inflammatory drug intake
_Other aesthetic procedure or skin traumatism less than 15 days before treatment
In the injected tissue, carbon dioxide reacts with water molecules, and then molecular carbonic acid is formed. This acid reduces the ph of the targeted tissue. There, the Bohr Effect comes into play – the lower the pH, the weaker the bond between hemoglobin and oxygen. While carboxytherapy is being applied, the release of oxygen from hemoglobin is increased in the site. Furthermore, at the level of pH of 6.8 and less the permeability of capillary walls is highly increased. At the pH of 6, 5, and less the flexibility of collagen fibers is increased, while their firmness is decreased [2-4,8-10,13]. Other chemical reactions include the reduction of divalent calcium ions and the split of carbonic acid to H+ and HCO3- resulting in the formation of the calcium hydrogen carbonate– Ca (HCO3)2, sodium hydrogen carbonate, and potassium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3 and KHCO3). As a routine reaction, pH becomes alkaline, which finally leads to an analgesic and spasmolytic effect. The tonus of arteries and capillaries is decreased because of these reactions and the skin temperature is increased by about 1°C. This effect combined with the changed activity of nerve endings improves the trophic of the treated localities. At the same time, oxidation of fats from the fat cells is activated more than usual, whereby some authors state that there is a direct lipolytic effect on adipocytes [6,8,9,12,20]. The residual CO2 is exhaled by the lungs. This treatment has other effects, the overall effects are also described, which lead to dilatation of coronary arteries, bradycardia, and decreased blood pressure. So it's better to have it under the protection of a specialist.

