Breast Augmentation (Breast Implants)

No country other than Iran is increasingly gaining ground and developing in plastic surgeries, particularly when it comes to Breast Augmentation; Iran has a lot to offer. Do not hesitate if you are considering Iran as your future destination to have Boob Job.
The top reason to have Breast Augmentation in Iran is undoubtedly its unrivaled price which can be found nowhere except in this country. Additionally, bear in mind that Iranian plastic surgeons are ranked among the best and most well-versed ones among their colleagues around the globe. Therefore, they are capable of bringing the most satisfactory outcomes if you decide to have your Breast Augmentation surgery in Iran.
Should you like to gain more information about Boob Job in Iran, please read on to find out further information respectfully.
What Is Breast Augmentation?
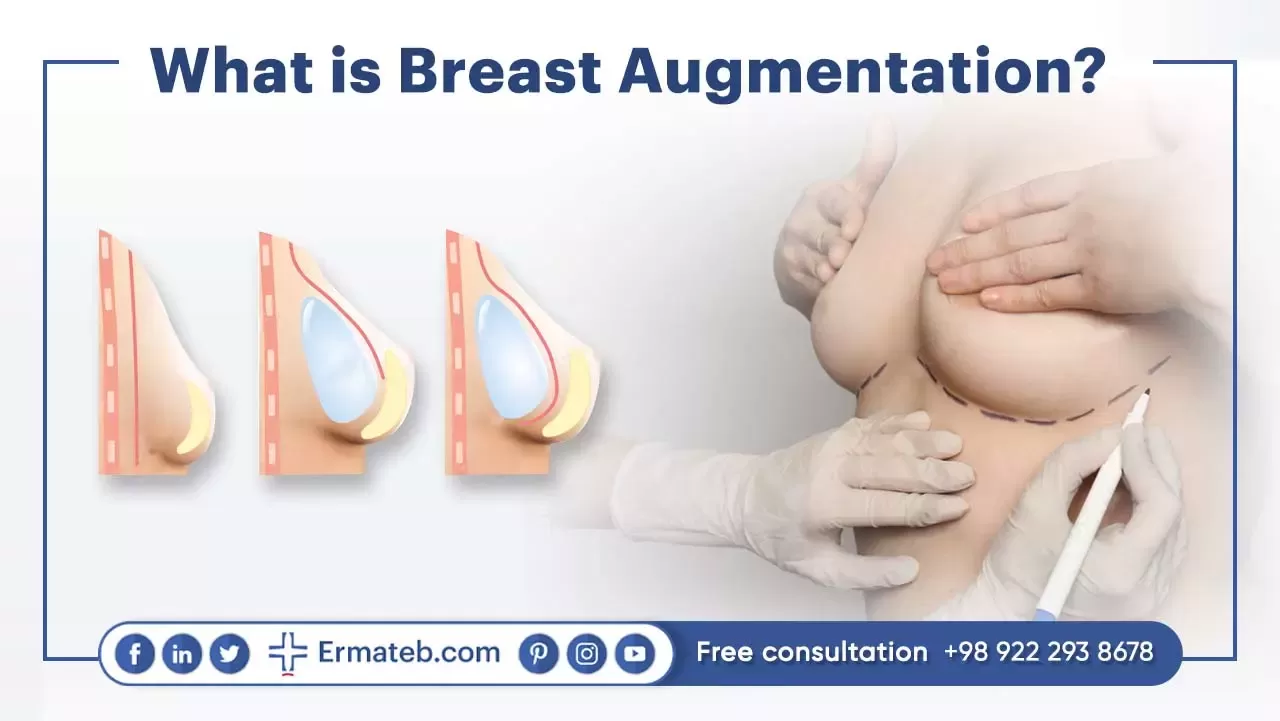
Breast Augmentation, also known as Breast Enlargement, is a transformative cosmetic surgery that enhances a woman’s bust size or reconstructs breasts post-mastectomy. The choice of implant type and size is influenced by factors such as desired breast size, anatomy, skin characteristics, and body shape.
This procedure involves placing implant either behind the breast tissue or beneath the chest muscle, resulting in improved breast cup size, shape, and overall appearance. Women seeking larger breasts or restoring volume lost after pregnancy and breastfeeding find this surgery beneficial. Surgeons consider various factors, including age, desired cup size, and rejuvenation needs, to tailor the procedure to individual preferences.
Breast augmentation contributes not only to physical transformation but also to increased confidence and self-esteem. The FDA mandates a minimum age of eighteen for saline-filled implants and twenty-two for silicone implants, aligning with the natural development of breasts until late teens or early 20s.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Breast Augmentation?
Achieving an ideal candidacy for breast augmentation involves several factors to consider, ensuring optimal results and patient satisfaction. Generally, good candidates for mammoplasty should be in good physical health, without active infections or serious illnesses. Breast augmentation is well-suited for those with sagging, flattered, or elongated breasts, lacking cleavage or volume, and those experiencing a loss of self-confidence due to smaller breasts.
To qualify for breast augmentation, individuals above 18 should meet specific criteria:
- Absence of life-threatening diseases, including diabetes, elevated blood pressure, cardiovascular issues, and blood coagulation disorders.
- No plans for future pregnancies.
- Non-smoker status.
- Realistic expectations about the surgery.
- Absence of depression or mental disorders.
- Saggy and small breasts due to aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, or hormonal fluctuations.
- Small breasts disproportionate to other body features.
- Small and asymmetrical breasts due to genetic factors.
- Loss of breast tissue due to trauma or cancer.
If you are dissatisfied with the loss of breast shape and volume post-weight loss, pregnancy, or aging, and if one or both breasts failed to develop normally, breast augmentation may be suitable, provided you are in good general health and have realistic expectations of improvement, not perfection.
Specific age requirements, such as being older than 18 for saline implants and older than 22 for silicone implants, also apply. Apart from the mentioned points, breast augmentation is suitable for women recovering from breast cancer who have lost breast tissue due to the disease, nonsmokers, those with finished size development, and individuals who are physically healthy with stable and normal weight.
As per the findings presented in the “Prospective Analysis of Primary Breast Augmentation on Body Image Using the BREAST-Q” article in the Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Journal, the utilization of breast implants has proven to be impactful in enhancing the overall quality of life for women. The study revealed noteworthy and enduring enhancements in satisfaction levels and psychosocial well-being among women who underwent breast augmentation with either Natrelle silicone-filled or saline-filled implants.
Who Should Not Have Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation may not be suitable for individuals with the following conditions:
- An abnormal mammogram
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding, or recent cessation of breastfeeding.
- Existing untreated breast cancer
- Severe illness or infection
For those with a family history of breast cancer, it is advisable to consult with our experts to determine the appropriateness of breast augmentation for individual circumstances.
Why Breast Augmentation in Iran?
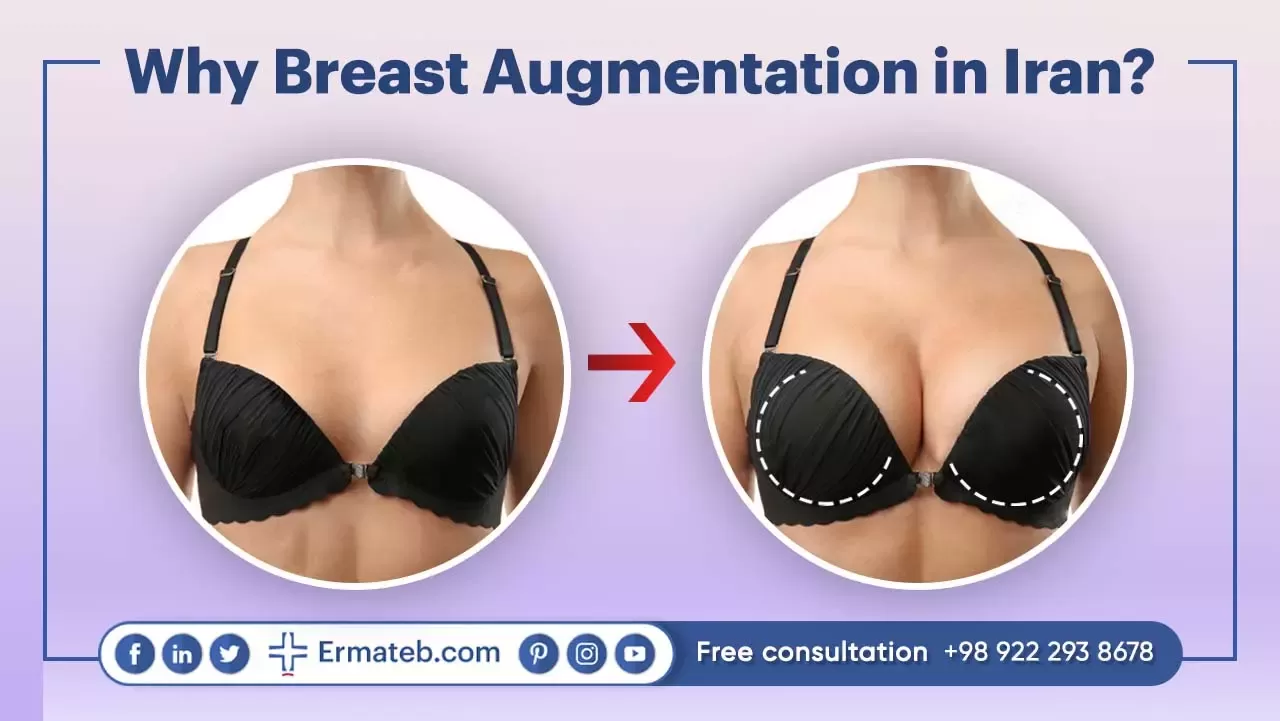
Iran has been drawing attention to plastic surgeries for the past few years. Iran has become the capital of aesthetic procedure in the Middle East. Many tourists choose Iran for surgeries like Breast Augmentation, Breast Lift, Breast Reduction, etc.
If you like to have Breast Augmentation but do not know where to go, read the reasons below why Iran is a good destination for Boob Job.
Affordable Price
Iran is, without any doubt, the cheapest destination for breast surgeries. This cheapness does not mean that you will not receive excellent services. In fact, by having Breast Augmentation in Iran, you can expect the same outcome and receive the same medical services as you have in the United States or any other country famous for Boob jobs. If you live in a country where aesthetic surgeries like breast implants are unreasonably high, you can have a trip to Iran, and the surgery will cost 2-4 times lower than what you have to pay in other places. If you are eager to know the exact prices, please read the "Breast Augmentation Price in Iran" section.
Highly Experienced and Adept Surgeons
In recent years, there has been a high demand for aesthetic surgeries like Breast Augmentation in various countries. Nevertheless, Iran is no exception in this regard.
Considering the new wave of interest in cosmetic procedures in Iran, Iranian plastic surgeons’ time is always occupied with many daily patients and operations. The number of surgeries an Iranian plastic surgeon performs daily equals the number of operations a plastic surgeon normally performs in two weeks in other countries. Therefore, most Iranian plastic surgeons are at the peak of their careers due to the number of surgeries performed and the experience and skills they have gained during these years.
A majority of Iranian plastic surgeons have attended the most prestigious and accredited Western universities and have passed their fellowships and specialized courses there. Further to this, most Iranian plastic surgeons are board-certified, being a member of medical-related associations like the Iranian Society of Plastic Surgeons, the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, or the International Society of Plastic Surgery. Therefore, you can leave your Breast Augmentation with ease to the hands of Iranian plastic surgeons whose skill, knowledge, and experience are main assets to their highly-reputed profession.
High-Quality Medical Services
Among a majority of people, there is an opinion that Iran is an underdeveloped country which is a total misconception flourished by the media and propaganda against the country. Regarding medical services, if you experience undergoing a medical or cosmetic procedure, it will surprise you how developed Iran is in this field.
In addition, Iran has clean and super-organized clinics, hospitals, and doctor's offices well equipped with the latest technology facilities. Do not doubt Iran is the best destination for a Boob Job, and you will not ever regret choosing Breast Augmentation in Iran. We assure you that you will be back to Iran for further surgeries once you have the chance to experience the quality of medical services in Iran, according to world standards.
Iran, a Great Destination for Tourists
If you are planning a trip to Iran to undergo a procedure, you will also have the opportunity to benefit from seeing the oldest civilization land in the world. At first sight, tourists usually fall in love with the Persian culture, food, local people, architecture, sights, and so many other wonders exceptional to this land. The top destinations where tourists can feel the authentic spirit of Iranian culture and history are Shiraz, Yazd, and Kashan by visiting the monuments left by Persian civilization.
Breast Augmentation Price in Iran
Iran is considered a prosperous country in attracting tourists' attention for medical/cosmetic surgeries. The main asset contributing to the country's success is the affordable cost Iran offers compared to other countries.
No one can deny the role of money in cosmetic procedures, especially Breast Augmentation, as one of the most expensive surgeries in every country. But the Breast Augmentation price in Iran is not comparable to any country, and many cannot believe their eyes that it is possible to achieve their desired breast size with such a price.
The cost of Breast Augmentation in Iran is something around $2,500- $3,000, which covers everything for a successful surgery, including doctor's visits, clinic, anesthesia, post-operative recovery, follow-up, etc. The cost of a Boob Job in Iran cannot be found anywhere else on this planet. If you don't believe it, let's see how much it costs if you have it in countries like Australia, Canada, Thailand, the United States, the United Kingdom, or Turkey.
The cost of Breast Augmentation surgery amounts to $12,000 in Australia, $10,000 in theUnited Kingdom, $7,000 in Canada, $6,000 in the United States, $4,500 in Turkey, and $4,000 in Thailand.
How Can I Get My Breast Implants Arranged in Iran?

Congratulations if you have decided to have Breast Augmentation in Iran. You may not know how to arrange your Boob Job in Iran, or you may probably have concerns like, "How am I supposed to speak the language in Iran" or "How can I arrange the surgery in the country?".
The critical factor of a successful medical procedure is simply the fact that patients must not be exposed to anxiety and stress, which is mainly due to insufficient information regarding the destination and how things will be there. Here is the point where medical facilitators play their major role. Ermateb, a leading medical facilitator in Iran, offers various medical and cosmetic services to patients worldwide.
Ermateb will surely help you with everything needed before your trip to Iran- our complex will assist you with obtaining the visa, booking the flight and accommodation, and transfer services, including Airport pickup and drop off and hotel transfer. Plus, upon your arrival, a personal interpreter and guide will be assigned to help you during your stay and the procedure up to the end of your journey in Iran.
For arranging your Breast Augmentation surgery with Ermateb, you should follow the steps described below:
- To reach Ermateb, you can contact us via one of our communication channels (WhatsApp or online form on the website)
- Next, a personal coordinator will be arranged to guide you through the following process of your medical/cosmetic procedure.
- Afterward, our consultant may ask for your medical records, documents, and other medical information will be required based on your personal qualities with the contribution of a surgeon.
- Lastly, after being briefed with all the necessary information, you can plan your trip to Iran if you would like to have a safe Breast Augmentation in Iran.
Different Techniques of Breast Augmentation in Iran
Breast augmentation encompasses various techniques aimed at enlarging and reshaping breasts, contributing to enhanced self-confidence and overall body satisfaction. Plastic surgeons perform these procedures in clinics or medical centers, employing different methods to achieve desired outcomes. Here are several breast augmentation techniques:
Breast Augmentation Mammoplasty
- Involves the use of breast implants or protheses to enlarge and reshape breasts.
- Silicone prostheses are placed under the skin to enhance size and aesthetics.
- Complementary therapies like breast lift may be employed to stabilize or enhance results.
Saline and Silicone Breast Implants
- Two main implant materials: saline and silicone gel.
- Saline implants contain sterile salt water and may be pre-filled or filled during the implant operation.
- Silicone gel implants, though more natural-feeling, carry additional risks if they leak.
- Implants come in different sizes, with smooth or textured shells, each having unique pros, cons, and complications.
Fat Injection
- An alternative for those averse to surgery, using fat transfer.
- Fat grafts are removed from unwanted areas (buttocks, thighs, abdomen) and injected into the breasts.
- Limited side effects compared to surgical options.
Gel Injection
- A popular choice with minimal invasiveness and rapid recovery.
- Gel injection behind the breast tissue provide a natural and lasting augmentation.
Breast Lift
- An option for those with sufficient breast tissue.
- Involves lifting breast tissue to a higher position for a more youthful appearance.
- Two methods: cutting and lifting breast tissue, or repositioning the nipple and breast tissue.
Breast Augmentation-Lift
- A combination of augmentation and lift techniques.
- Suitable for achieving both fullness and correcting nipple positioning.
- Requires thorough consultation with a plastic surgeon to determine suitability.
What Are the Different Types of Breast Implants?
Breast implants offer a range of options, categorized by ingredients, shape, and surface texture. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for individuals considering breast augmentation. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Ingredients and Shapes
- Breast implant come into two main types: Saline and Silicone.
- Saline Implants are filled with sterilized salt water, providing a natural absorption process in care of leakage.
- Silicone gel implants, on the other hand, offer a more realistic feel but necessitate careful monitoring due to potential gel leakage.
In terms of shape:
- Teardrop-shaped implants mimic a natural body contour but raise concerns about rotation.
- Round implants are symmetrical, ideal for accentuating upper breast portions without rotation-related issues.
Surface Texture
- Smooth-surfaced implants are softer and more mobile, offering increased comfort but may be slightly palpable or show visible creases.
- Textured implants have a rough surface that aids attachment to surrounding tissues, providing a more secure fit.
Comparing Saline and Silicone Implants
Both implant types share similarities:
- Approved by the FDA and considered safe.
- Durable, with a lifespan of 10-20 years.
- Outer shell made of silicone.
Key differences include:
- Silicone implants feel more natural.
- Saline implants are more economical.
- Age requirements: 18 for saline, 22 for silicone.
Further Implant Varieties
- Cohesive Silicone Implants: known as “gummy bear” implants, they are softer, longer-lasting, and feature a strong silicone shell.
- High-Profile Breast Implants: Ideal for those with a narrower chest frame, offering a considerable size increase while maintaining a natural shape.
Things to Consider Before Performing Breast Augmentation in Iran
You must consult with a plastic surgeon about your preferences for the size and appearance of your breasts. The surgeon will inform you of specific types of implants and effective techniques. Before having this surgery, consider the following issues:
- Breast implants won’t avoid your breasts from sagging. To correct sagging breasts, you may need a breast lift in addition to breast augmentation.
- Breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime. The average life span of an implant is ten years. Furthermore, your breasts will continue to age, and factors such as weight gain or weight loss may change the appearance.
- Insurance does not cover breast implants unless it is medically necessary.
- You might need additional surgery if you want your breast implant removed.
Preoperative Steps Before Breast Augmentation in Iran
Embarking on the transformative journey of breast augmentation in Iran necessitates thorough preoperative considerations and meticulous preparation. The process involves a multifaceted approach to ensure optimal outcomes and a smooth recovery:
- Engage in counseling with cosmetic or plastic surgeons in Iran.
- Discuss desired breast size and address breast asymmetry.
- Recommendations may include varying implant sizes or different fat volumes for uniformity.
- Refraining from smoking for optimal preoperative conditions for a minimum of five weeks.
- Providing a comprehensive understanding of existing diseases, medications and lifestyle for necessary adjustments.
- Adhere to surgeon’s instructions, including advisories against consuming food or drink 15 days before surgery to mitigate bleeding risks.
- Fasting for eight hours before surgery.
- Discontinuing certain medications, supplements, tobacco, or alcohol for at least two weeks.
- Emphasize the importance of obtaining a baseline mammogram both before and after surgery.
- Choose a qualified and experienced surgeon with knowledge about breast implants, anatomy, and surgical techniques.
- Conduct thorough research to identify the right breast implant brand.
- Communicate food or drug allergies during consultation sessions.
- Abstain from NSAIDs, blood-thinning medications, herbal medications, teas, and dietary supplements containing vitamin E.
- Manage weight concerns by initiating weight loss at least three months before the operation to prevent postoperative sagging or deformities.
In summary, this comprehensive guide outlines key preoperative measures for breast augmentation, ensuring patients are well-prepared, informed, and positioned for a successful and transformative experience in Iran.
What Does Breast Augmentation Surgery Involve in Iran?
Generally, Breast Augmentation surgeries are usually performed in a surgical center or hospital outpatient facility. You can go home the same day following the operation, though a hospital stay is required in some rare cases.
Patients should be aware that they should not be exposed to too much stress and anxiety before any medical surgery. That is why medical facilitators like Ermateb come into play in order to simplify the process, starting from the very moment the patients arrive till they leave the country with satisfaction.
Below, we have described the procedure depicting in detail what exactly happens step by step before, during, and after Breast Augmentation surgery in Iran.
Before the Procedure
- Before the operation, you will consult with your surgeon about your preferences for the size, feel, and appearance of your breasts.
- Your surgeon will explain different types of breast implants including smooth or textured, round or shaped like teardrop, saline or silicone – as well as options for surgical techniques.
- You will be required to have a breast screening (baseline mammogram) before the surgery by your surgeon.
- Your doctor might adjust certain medications before the operation; for example, you have to avoid aspirin or other drugs that can increase bleeding.
- If you are a smoker, your surgeon will ask you to stop smoking for a time which is typically 4-6 weeks before and after the surgery. You will also be advised to avoid alcoholic drinks before the operation.
During the Procedure
- Anesthesia: Breast Augmentation can be done under local anesthesia in which you are awake and the breast area is numb, though the surgery is often done during general anesthesia – you are asleep for the surgery. However, your plastic surgeon will share different anesthesia options with you before the surgery.
- Making Incisions: The surgeon will make an incision in one of three places to insert the breast implant (These 3 places are the crease under the breast, under the arm, and around the nipple).
- Inserting Implants: After the incision is made, the surgeon will separate the breast tissue from the muscles and connective tissue of the chest. This creates a pocket either behind or in front of the outermost muscle of the chest wall (called the pectoral muscle). Then, the surgeon inserts the implant into this pocket and centers it behind the nipple.
- Closing Incisions: When the implant is in place, the surgeon will close the incision- typically with sutures- and bandage it with skin adhesive and surgical tape.
After the Procedure
- Following Breast Augmentation surgery, you will be taken to a recovery room where hospital nurses closely monitor you for any rising complications.
- You will probably experience soreness and swelling, which are likely for a few weeks after the surgery. Your surgeon will also prescribe medication to soothe the post-operative pains felt after a Boob Job.
- To expedite the healing process, you should wear a compression bandage or sports bra for extra support and positioning of the breast implant.
- You might be able to return to work within a few weeks if you do not have a physically demanding job. You should stay away from strenuous activities that could raise your pulse or blood pressure for at least 2 weeks. Note that your breasts will be sensitive to physical contact or jarring movements.
- If your surgeon used unabsorbable sutures or placed drainage tubes near your breast, you would need a follow-up appointment for removal.
- Patients sometimes notice warmth or redness in the breast, which is probably an infection. Therefore, if you have these symptoms after the surgery, contact your surgeon as soon as possible. In addition, you ought to contact your doctor if you have shortness of breath or pain in the chest.
Non-Surgical Methods of Breast Augmentation in Iran
Apart from surgical methods, there are some alternative methods for breast augmentation in Iran that steer clear of surgery and its associated risks, albeit with a longer duration to witness results. Various non-surgical techniques are available to enhance breast size and appearance:
1. Acupuncture:
Acupuncture emerges as a non-surgical option for breast augmentation, demonstrating the ability to significantly increase breast size within a relatively short timeframe.
2. Herbal Medicines:
Herbal medicines enriched with herbal estrogen are designed to stimulate breast augmentation naturally, offering a non-invasive alternative.
3. Breast Enhancement Creams and Lotions:
Specially formulated creams and lotions contribute to natural breast enlargement by harnessing the benefits of herbal ingredients. These products also work to enhance firmness and tightness.
4. Breast-Enhancing Exercises:
Incorporating breast-enhancing exercises, commonly referred to as push-ups, becomes a non-surgical means of enlarging breasts by targeting and strengthening the underlying breast muscles.
While these methods bypass the need for surgery, it is essential to note that results may take more time to manifest compared to surgical interventions such as breast lift, breast augmentation, and breast prosthesis.
What Is Breast Augmentation Recovery Like?
Typically, patients probably feel weak after the surgery. If you have a Boob job, you will probably feel sore for 2-3 weeks, and you will likely have a lot of swelling. You will also have a pulling or stretching feeling in your breast in the first few days following the Breast Augmentation surgery. You can expect to feel better and stronger as the days go by, although you may need to take pain-killer medications for at least a week or two. Additionally, you may get tired quickly or have less energy than usual most of the time, which might last several weeks after the operation.
The stitches on your breasts would be taken out in 7-14 days after the surgery if your surgeon closed the incisions with removable stitches.
The new breasts will feel firmer and look rounder after a few weeks and the skin on the breasts may also be numb for a short period. Your new breasts will get better with time, and the permanent feeling of pain will fade away in the nipple area.
If you like to have a quicker recovery resulting in better outcomes, you'd better follow the steps below, categorized as do' s and don'ts in terms of activity, diet, and medicines.
Activity
- Get enough sleep and rest whenever you feel tired.
- Avoid lifting anything that would make you strain for about 4-6 weeks.
- Do not lift anything over your head for 2-3 weeks.
- Ask for your doctor’s consent when it is okay to have sexual activity.
- Ask your doctor when is the proper time for driving.
- It is okay to take a shower the day after the operation on the condition that you do not have a drain near your incision. You can shower the day after the drain is removed.
- Do not soak in the bathtub for about 4 weeks.
- Sleep on your back with your head and shoulders lifted with a pillow. This will help keep your implants in place and prevent them from slipping or shifting.
- You might be able to return to work and life routine within 1-2 weeks. However, it depends on the type of work you do and any further treatment.
- Try to walk each day and start walking a little more than you did the day before. Regular walking boosts your blood flow and helps prevent pneumonia and constipation.
- Stay away from strenuous activities, such as jogging, bicycle riding, weight lifting, or aerobic exercise; you can do them unless your doctor consents to do so.
Diet
- After the surgery, you can have your normal diet. If your stomach is upset, you can try bland and low-fat foods like broiled chicken, plain rice, toast, and yogurt.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- You may notice that your bowel movements are not regular after the surgery. In fact, this is common; therefore, try to avoid constipation and straining with bowel movements. Take a mild laxative if you have not had a bowel movement after a couple of days.
Medicines
- Follow your doctor's instructions, and he/she will tell you when to restart your medicines. Also, your doctor will give you the necessary instructions about taking any new medication.
- If you stop taking blood thinner medicines like aspirin, your doctor will tell you when to start retaking them.
- Take the pain-killer medicines prescribed by your doctor. Ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter medicine.
- If you think that your pain medicine makes you feel sick in the stomach, either take your medicine after meals or consult with your doctor for a different pain-killer
- Take regularly your prescribed antibiotics by your doctor. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take an entire course of antibiotics to help with a quicker recovery.
Risks and Complications of Breast Augmentation
Before undergoing breast augmentation surgery, it’s essential to comprehend the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. Your medical team will provide detailed information and ask you to sign consent forms to ensure your understanding of the surgery’s nuances.
Common risks involved in breast augmentation surgery encompass:
- Anesthesia risks
- Hematoma
- Bleeding
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation
- Infection
- Persistent pain
- Incorrect implant positioning
- Formation of tight scare tissue (capsular contracture)
- Poor scaring
- Implant leakage or rapture
- Fluid Accumulation (seroma)
- Skin wrinkling over the implant
- Necessity of revision surgery
Before undergoing breast augmentation surgery, it’s essential to comprehend the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. Your medical team will provide detailed information and ask you to sign consent forms to ensure your understanding of the surgery’s nuances.
It’s crucial to note that breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime. Factors like pregnancy, weight loss, and menopause can impact the appearance of augmented breasts over time. Surgeons recommend follow-up appointments to evaluate breast condition, and additional surgeries may be required to replace implants.
Additionally, typical risks and complications associated with breast augmentation include temporary pain, swelling, bruising, blood clots, sensitivity to anesthesia, and hematoma formation. Complications may involve changes in nipple or breast sensation, implant rotation, rupture or leakage, a feeling of tightness, reduced breast milk production, and the development of tight scar tissue (capsular contracture).
While some complications may be temporary and resolve over time, others depend on individual physiological characteristics. A skilled surgeon and proper implant selection contribute significantly to minimizing discomfort and unwanted side effects. Specific risks include capsular contracture, skin folds/creases, wound infection, improper wound healing, bleeding, serve scarring, and potential damage to the implant, along with changes in sensitivity. Always express your concerns and expectations to your surgeon for optimal results.
The Results of Breast Augmentation in Iran
While the immediate impact of breast augmentation in Iran is visibly larger breasts, achieving the ultimate results requires patience as swelling diminishes, and the skin undergoes tightening. Patients with asymmetrical or notably small breasts may utilize a bandage to shape their breasts during the initial stages. The process of incision scars fading might extend over several months to a few years.
In cases of fat transfer breast augmentation, a minor portion of the injected fat may be naturally absorbed by the body. Generally considered permanent, the longevity of fat transfer results is influenced by various factors, such as the surgeon’s skill and experience, the fat source, its type, and the precise injection method.
Maintaining your post-surgery weight is crucial for optimal and enduring results. However, it’s important to acknowledge that breast tissue and fat levels may naturally undergo changes with age, despite efforts to preserve the initial outcome.


 Arabic
Arabic
 German
German
 Persian (Farsi)
Persian (Farsi)
 Russian
Russian
 Beauty
Beauty


 Medical
Medical




 Hotels
Hotels
 Hospitals
Hospitals



























![Frequently asked question about [name]](/v2tem/images/pages/service/faq-image.webp)
